T. Lilly Golda
Assistant Professor of English
A.P.C. Mahalaxmi College for Women
Thoothukudi
golda.albert@gmail.com
Introduction
Worldwide research has identified a sort of anxiety which is often associated
with second language learning. MacIntyre and Gardner (1994: 284) described
second language anxiety as “the feeling of tension and apprehension
specially associated with second language contexts, including speaking, listening,
and writing”. Experts on ELT (English Language Teaching) claim that
writing is indeed a difficult skill to acquire. Learning to write is a long-term
process. The progress of students is painfully slow. Despite years of learning
English, students fail miserably. Teaching and learning writing involve stressful
situations. The main concern of the teacher is to make the students communicate
effectively. It is crucial to establish a learning environment where students
can write in their second language without embarrassment. Hence the researcher
sought to observe the various levels of writing skills of students belonging
to different arts and science colleges in Manonmaniam Sundaranar University,
Tirunelveli, and analyzes the causes for writing anxiety.
Aim
The present study aims to answer the following research questions about ESL
(English as a Second Language) writing anxiety.
1. Is there any second language writing anxiety among the student samples?
2. What are the main factors that cause ESL writing anxiety?
Research setting and participants
of the survey
The first phase of the research was undertaken at eight colleges of arts and
science affiliated to Manonmaniam Sundaranar University, Tirunelveli. There
are many arts and science colleges in all and the scope of the study was restricted
to eight colleges. Three southern districts were represented in the survey.
As many as 800 students participated in the survey. Most of the students belonged
to rural areas and considered their second language (L2), a difficult one.
Material and methods
The Second Language Writing Anxiety Inventory (SLWAI) (Cheng, 2004)
was adapted to assess the level of ESL writing anxiety among the students.
The participants were asked to indicate the extent to which they agreed or
disagreed with the statement on a 5-point Likert response scale from 1 (strongly
disagree) to 5 (strongly agree). This constituted
Questionnaire I.
The Second Language Writing Anxiety Inventory (SLWAI) was developed by Cheng
in 2004. The SLWAI consists of 22 items, scored on a Five-point Likert response
scale ranging from 1 (strongly disagree) to 5 (srongly agree). Five of the
items (1,4,17,18,22) are negatively worded and require reverse scoring before
being summed up to yield total scores. A higher score obtained thereupon indicates
a high level of writing anxiety, a total score below 50 points indicates a
low level of writing anxiety, and a total score in-between indicates a moderate
level of writing anxiety. The 22 items of the SLWAI can be divided into three
categories of anxiety, such as Cognitive Anxiety (1,3,7,9,14,17,20,21), Somatic
Anxiety (2,6,8,11,13,15,19), Avoidance Behaviour (4,5,10,12,16,18,22). Cognitive
Anxiety refers to the mental aspect of anxiety experience, including negative
expectations, preoccupation with performance and concern about others’
perception. (Cheng, 2004: 316). Somatic Anxiety refers to one’s perception
of the physiological effects of the anxiety experience, as reflected in increase
in arousal of unpleasant feelings, such as nervousness and tension. (Cheng,
2004: 316). Avoidance behaviour refers to the behavioural aspect in the avoidance
of writing. (Cheng, 2004: 316). The statements of the original 22 items were
modified by the researcher to suit the Indian context.
Questionnaire II consisted of open ended questions. The purpose of these questions was to gather in-depth information about students’ writing experiences and reasons for writing anxiety. The questionnaire was designed to find out the most common factors that cause ESL writing anxiety among students in English writing practice.
Following are the questions:
How often do you write?
What do you think are the causes of writing anxiety?
In what ways do you think you can improve your writing skills?
Statistical techniques used
The answers to Questionnaire I-the SLWAI were
analyzed with SPSS (Statistical program for Social Science) to obtain the
levels and types of ESL writing anxiety experienced by the students.
For the analysis of Questionnaire II, the investigator used percentage analysis.
The formula used to calculate the percentage was as follows:

Analysis and discussion
In this section, the data collected from the two questionnaires have been presented and analyzed. In the first section, the results of two questionnaires are presented in tables. In the second section, there is an in-depth analysis and discussion about the results. Answers to the two research questions are found out as well in this section.
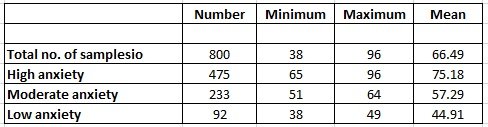
Table 1 presents descriptive statistics of the SLWAI, which shows a high level of ESL writing anxiety (Mean=66.49,>65) among the student samples. The possible scores on the SLWAI range from 22 to 110. The participants’ scores in this study ranged from 38 to 96. The mean score was 66.49, which reflected a high level of anxiety. In addition, 475 students (59%) were found to have high levels of anxiety, which might reinforce the conclusion that there is a high level of L2 writing anxiety among the students.
Table 1. Descriptive statistics of the SLWAI:
The types of SLWA
The SLWAI offers a three-dimensional conceptualization of anxiety, such as Somatic Anxiety, Cognitive Anxiety, and Avoidance Anxiety (Cheng, 2004). The distribution of the three types of writing anxiety is presented in the following table:
Table 2: Descriptive statistics of the Types of SLWA
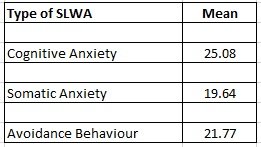
This table shows that Cognitive Anxiety is the most common type of SLWA, followed by Avoidance Behaviour.
Causes of ESL writing anxiety
Research question 2 sought to seek answers to the following
question:
What are the main causes of writing anxiety?
It was inferred from the responses of the students that only a negligible
number of them wrote in English. Even those who did so, did it only when there
was a compulsion and not out of interest. When it came to preparing essays
pertaining to the syllabus, students preferred the ones passed on by the teacher
or their classmates. Most of their composition work too was not original.
The main causes of ESL writing anxiety as stated by the student sample have been categorized and presented below.
Majority of the students claimed that they were from Tamil medium schools and that they had minimum exposure to English. Even those who had been from English medium schools had insufficient writing practice which caused them writing anxiety. Since they did not have good reading habits, they lacked topical knowledge too thus increasing their level of anxiety. Few of them had low self-confidence. Since there had been no motivation at all they had never attempted to write. The investigator identified that students became anxious when they had difficult experiences with writing. These struggles might be due to fear of negative evaluation, lack of effective feedback or discouragement.
These observations echo the findings of Kara (2013: 109) that: “When writing as a skill is considered, learners thought that they lack necessary strategies like organizing ideas, gathering information, combining ideas. Moreover they thought that their English is not enough to express themselves clearly”.
Conclusion
The main findings obtained from this study can be summarized as follows:
1) There is a high level of ESL writing anxiety among the student samples; among the three types of ESL writing anxiety, the Cognitive Anxiety is the most common anxiety.
2) Lack of exposure to English and insufficient writing practice constitute the main sources of ESL writing anxiety experienced by the students.
Anxiety no doubt affects the process of learning. Writing anxiety impedes communication. It needs a lot of practice to overcome this anxiety. Learners should understand that as they confront more and more new situations they will gradually be able to overcome their writing anxiety. Teachers too should expose learners to English and make them feel comfortable while teaching writing.
Works cited
Cheng, Y. S. (2004). A measure of second language writing anxiety: Scale development and preliminary validation. Journal of Second Language Writing. vol. 13, pp. 313-15.
MacIntyre, P.D., & and Cardener, R. C. (1994). The subtle effects of language anxiety on cognitive processing in the second language. Language Learning. Vol. 44, no. 2, pp. 283-305
Kara, Selma. (2013). Writing anxiety: A case study on students’ reasons for anxiety in writing classes. Anadolu Journal of Educational Sciences International. January 2013, 3(1), pp. 103-111